
-
МјРЇСІИёСЖШИМі
-
 И№ОЫ КИОЫ Йъ ЗЛЦЎЧЯБт~ ИЎСЖЦЎ ПЙОрБюСі
И№ОЫ КИОЫ Йъ ЗЛЦЎЧЯБт~ ИЎСЖЦЎ ПЙОрБюСі 89,611
89,611 -
 [ЧЪИЎЧЩ ММКЮ] ФЋИ№ХзНК ПЉЧр 100Йш СёБтБт
[ЧЪИЎЧЩ ММКЮ] ФЋИ№ХзНК ПЉЧр 100Йш СёБтБт 49,796
49,796 -
 ИЖДвЖѓ НУГЛ - ИЎРп АјПјСЄКИ. (ЛчСј 16Рх ЦїЧд)
ИЖДвЖѓ НУГЛ - ИЎРп АјПјСЄКИ. (ЛчСј 16Рх ЦїЧд) 30,847
30,847 -
 ММКЮРЧ СіПЊСЄКИ15,561
ММКЮРЧ СіПЊСЄКИ15,561 -
 ИЖДвЖѓ БйБГ - ЕћАЁРЬЕћРЬ ПЉЧр СЄКИ14,403
ИЖДвЖѓ БйБГ - ЕћАЁРЬЕћРЬ ПЉЧр СЄКИ14,403 -
 [ЧЪИЎЧЩ ММКЮ/ИЗХК] ШЃХк МїЙк ПфБн Йз СЄКИ13,357
[ЧЪИЎЧЩ ММКЮ/ИЗХК] ШЃХк МїЙк ПфБн Йз СЄКИ13,357 -
 КИЖѓФЋРЬРЧ И№Еч И№НРРЛ КММі РжДТ ЛчСјУИ.13,168
КИЖѓФЋРЬРЧ И№Еч И№НРРЛ КММі РжДТ ЛчСјУИ.13,168 -
 ИЖДвЖѓ БйБГ - ЦХЛѓЧб ЦјЦї ПЉЧрСЄКИ12,869
ИЖДвЖѓ БйБГ - ЦХЛѓЧб ЦјЦї ПЉЧрСЄКИ12,869 -
 [ММКЮ-ЙшМБТјРх] МБЙкШИЛч РќШЙјШЃПЁПф~12,495
[ММКЮ-ЙшМБТјРх] МБЙкШИЛч РќШЙјШЃПЁПф~12,495 -
 ИЖДвЖѓ СіПЊ(ПЁИЃЙЬХИ -ИЛЖѓХз)РЧ СіЕЕ/ЧбБЙ РННФСЁ/МюЧЮИє12,147
ИЖДвЖѓ СіПЊ(ПЁИЃЙЬХИ -ИЛЖѓХз)РЧ СіЕЕ/ЧбБЙ РННФСЁ/МюЧЮИє12,147
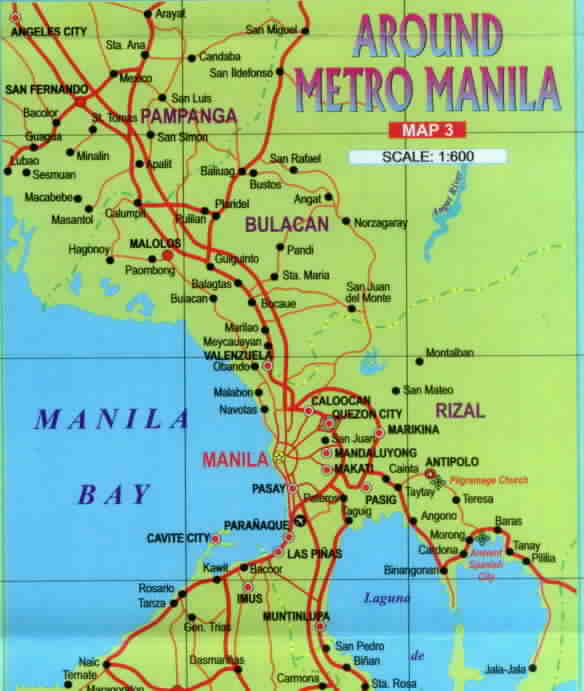
Manila Bay is a natural harbor which serves the Port of Manila (on Luzon), in the Philippines.The bay is
considered to be one of the best natural harbors in Southeast Asia and one of the finest in the world.
Strategically located around the capital city of the Philippines, Manila Bay facilitated commerce and trade
between the Philippines and its neighbouring countries[1], becoming the gateway for socio-economic
development even prior to Spanish occupation. With an area of 1,994 km2 (769.9 sq mi), and a coastline of
190 km (118.1 mi), Manila Bay is situated in the western part of Luzon and is bounded by Cavite and
Metro Manila on the east, Bulacan and Pampanga on the north, and Bataan on the west and northwest.
Manila Bay drains approximately 17,000 km2 (6,563.7 sq mi) of watershed area, with the Pampanga River
contributing about 49% of the freshwater influx. With an average depth of 17 m (55.8 ft), it is estimated to have a
total volume of 28.9 billion cubic meters (28.9 cubic km). Entrance to the bay is 19 km (11.8 mi) wide and expands to a width of 48 km (29.8 mi). However, width of the bay varies from 22 km (13.7 mi) at its mouth and expanding to 60 km (37.3 mi) at its widest point.
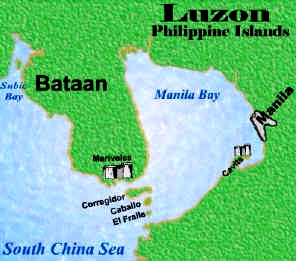
The islands of Corregidor and Caballo divides the entrance into two channels[2], about 2 miles (3.2 km) towards the North and 6.5 miles (10.5 km) wide on the South side. Mariveles, in the province of Bataan, is an anchorage
just inside the northern entrance and Sangley Point is the former location of Cavite Naval Base. On either side
of the bay are volcanic peaks topped with tropical foliage: 40 km to the north is the Bataan Peninsula and to the
south is the province of Cavite.
Across the entrance to Manila Bay are several islands, the largest of which is Corregidor, located 3 kilometers
from Bataan and, along with the island of Caballo, separates the mouth of the bay into the North and South
Channels. In the south channel is El Fraile Island and outside the entrance, and to the south, is Carabao Island. El Fraile, a rocky island some 4 acres (1.6 ha) in area, supports the massive concrete and steel ruins of
Fort Drum, an island fortress constructed by the United States Army to defend the southern entrance of the bay.
To the immediate north and south are additional harbors, upon which both local and international ports are
situated. Large number of ships at the North and South harbors facilitate maritime activities in the bay.
Being smaller of the two harbors, the North Harbor is used for inter-island shipping while the South Harbor is used for large ocean-going vessels.
History
Manila Bay was connected to Laguna Lake (or Laguna de Bai) approximately 3,000 years ago.Recurring
episodic uplifts along the West Marikina Valley Fault caused the two to break up. Interaction between Manila
Bay and Laguna Lake occurs only through Pasig River.
The bay was the setting for the Battle of Manila Bay in 1898 in which American troops led by Commodore
George Dewey, seized the area. Significantly, this battle showcased the United States' naval strength when
all major Spanish ships were destroyed and captured.With its proud historic past and the place brimming with
marine life[5], Manila Bay became the ocean portal to its epicenter for government, economy and industry.
Corregidor Island was annexed by Japanese forces fighting from this bay once again in 1942. Even earlier
various other battles were fought from this naval base including the La Naval de Manila in 1646, which finally put a stop gate to the Dutch trials to seize the Philippines.
Today, Manila Bay still remains important for commerce and industry, including fishing, although rapid urban
growth and industrialization are contributing to a decline in water quality and deteriorating marine habitats. It also serves a focus for recreation for Metro Manila and is a popular destination for walks and for viewing the sunset. Much of the land fronting the bay along Metro Manila is reclaimed land which now includes important sites such as the Philippine Senate and the Mall of Asia.
On September 27, 2011, The sea walls of Manila Bay were destroyed by the storm surge caused by Typhoon Pedring, making the baywalk area devastated. Even the US Embassy, Museo Pambata and Sofitel Philippine Plaza were submerged into flooding. It was estimated that the damage would cost P30 million.
- ЁЄ
- ЁЄ
- ЁЄ
- ЁЄ
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet\'\"\\(
- ЁЄryWvMVxeetщ\'\"\\(
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet














 ЧЪРкДхФФ ОпАЃЛѓДу ПРЧТ
ЧЪРкДхФФ ОпАЃЛѓДу ПРЧТ 13ГтПЌМг МвКёРкИИСЗ 1РЇ
13ГтПЌМг МвКёРкИИСЗ 1РЇ

 ГЛАд ИТДТ ОюЧаПј УЃБт
ГЛАд ИТДТ ОюЧаПј УЃБт
 ИЎОѓ ЧаБГ ЙцЙЎБт
ИЎОѓ ЧаБГ ЙцЙЎБт
 СжИЛПЁ ГЛАЁ ОЕ КёПыРК?
СжИЛПЁ ГЛАЁ ОЕ КёПыРК? УжАэАЁМККё РЬКЅЦЎ СёБтБт
УжАэАЁМККё РЬКЅЦЎ СёБтБт
 ЧіСіПЁМЕЕ ЧЪРкДхФФ!
ЧіСіПЁМЕЕ ЧЪРкДхФФ! ЧіСіПЁМ АЁДЩЧб
ЧіСіПЁМ АЁДЩЧб









 ЧЪРк ЦЏБо Ч§ХУ! ФСНУОюСі МКёНК
ЧЪРк ЦЏБо Ч§ХУ! ФСНУОюСі МКёНК
































