
-
МјРЇСІИёСЖШИМі
-
 И№ОЫ КИОЫ Йъ ЗЛЦЎЧЯБт~ ИЎСЖЦЎ ПЙОрБюСі
И№ОЫ КИОЫ Йъ ЗЛЦЎЧЯБт~ ИЎСЖЦЎ ПЙОрБюСі 89,738
89,738 -
 [ЧЪИЎЧЩ ММКЮ] ФЋИ№ХзНК ПЉЧр 100Йш СёБтБт
[ЧЪИЎЧЩ ММКЮ] ФЋИ№ХзНК ПЉЧр 100Йш СёБтБт 50,428
50,428 -
 ИЖДвЖѓ НУГЛ - ИЎРп АјПјСЄКИ. (ЛчСј 16Рх ЦїЧд)
ИЖДвЖѓ НУГЛ - ИЎРп АјПјСЄКИ. (ЛчСј 16Рх ЦїЧд) 30,907
30,907 -
 ММКЮРЧ СіПЊСЄКИ15,588
ММКЮРЧ СіПЊСЄКИ15,588 -
 ИЖДвЖѓ БйБГ - ЕћАЁРЬЕћРЬ ПЉЧр СЄКИ14,496
ИЖДвЖѓ БйБГ - ЕћАЁРЬЕћРЬ ПЉЧр СЄКИ14,496 -
 [ЧЪИЎЧЩ ММКЮ/ИЗХК] ШЃХк МїЙк ПфБн Йз СЄКИ13,411
[ЧЪИЎЧЩ ММКЮ/ИЗХК] ШЃХк МїЙк ПфБн Йз СЄКИ13,411 -
 КИЖѓФЋРЬРЧ И№Еч И№НРРЛ КММі РжДТ ЛчСјУИ.13,214
КИЖѓФЋРЬРЧ И№Еч И№НРРЛ КММі РжДТ ЛчСјУИ.13,214 -
 ИЖДвЖѓ БйБГ - ЦХЛѓЧб ЦјЦї ПЉЧрСЄКИ12,920
ИЖДвЖѓ БйБГ - ЦХЛѓЧб ЦјЦї ПЉЧрСЄКИ12,920 -
 [ММКЮ-ЙшМБТјРх] МБЙкШИЛч РќШЙјШЃПЁПф~12,543
[ММКЮ-ЙшМБТјРх] МБЙкШИЛч РќШЙјШЃПЁПф~12,543 -
 ИЖДвЖѓ СіПЊ(ПЁИЃЙЬХИ -ИЛЖѓХз)РЧ СіЕЕ/ЧбБЙ РННФСЁ/МюЧЮИє12,198
ИЖДвЖѓ СіПЊ(ПЁИЃЙЬХИ -ИЛЖѓХз)РЧ СіЕЕ/ЧбБЙ РННФСЁ/МюЧЮИє12,198
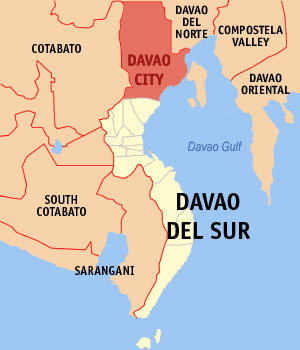
The City of Davao, the de facto capital of MindanaoCebuano: Dakbayan sa Dabaw ; Tagalog: Lungsod ng
Dabaw ; Spanish: Ciudad de Davao) is the largest city in the island of Mindanao in the Philippines. Its international airport and seaports are among the busiest cargo hubs in the Philippines.
Davao City is also one of several cities in the Philippines that are independent of any province. The city serves
as the regional center of Davao Region (Region XI) and the metropolitan center of Metro Davao. It has a population of 1,464,301 according to 2010 LGPMS Census, making it the country's largest city outside Metro Manila and
the second overall with the cities of Metro Manila combined. In recent years, Davao City has emerged as the
financial-capital, investment and tourism hub for the entire southern Philippines. The City Mayors Foundation
ranks Davao City as the 87th fastest growing city in the world,and it has been listed by the Foreign Direct Investment Magazine as the 10th "Asian City of the future".
The city has numerous beaches and mountain resorts. It is a home of the highest mountain in the Philippines
which is Mt. Apo. It is named as the Durian and Mangosteen Capital of the Philippines since these fruits were locally cultivated mostly in this city and are sold and exported for both home and abroad; it is also known as the Philippines' Sashimi Capital because sashimis are the big industry in the city, the kinilaw, is the most
common food often served at restaurants and even at homes here in this city.
History
Name's history
Local historians of Davao claim that the word davao came from the phonetic blending of the word of three
Bagobo subgroups when referring to Davao River, an essential waterway which empties itself into Davao Gulf
near the city. The aboriginal Obos who inhabit the hinterlands of the region called the river, Davoh; the Clatta or
Guiangans called it Duhwow, or Davau, and the Tagabawa Bagobos, Dabu. To the Obos, the word davoh also
means a place "beyond the high grounds", alluding to the settlements located at the mouth of Davao River which were surrounded by high rolling hills. When asked where they were going, the usual reply is davoh, while pointing towards the direction of the town. Duhwow also refers to a trading settlement where they barter their forest
goods in exchange for salt or other commodities.
Population
| Population Census | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | Rate | |
| 1980 | 614,124 |
| |
| 1990 | 849,947 | 3.3% | |
| 1995 | 1,006,840 | 3.4% | |
| 2000 | 1,147,116 | 2.84% | |
| 2007 | 1,363,337 | 2.41% | |
| Est. 2010 | 1,464,301 | 27.65% | |
The estimated population of the city is 1,464,301 in 2010 according to 2010 LGPMS Census. Metro Davao,
with the city as its metropolitan center, has about 2,274,913 people in 2010, making it as the third most populous metropolitan agglomeration in the Philippines and the most populous and cleanest city in Mindanao; also as of
2010, the total population of the city's local government agglomeration (including other LGU's outside Metro
Davao such as Sto. Tomas and Kapalong in Davao del Norte and Bansalan in Davao del Sur) is estimated to
about 2,854,711. However, an estimated number of between 2-4 million people are present in Davao City during
the daytime owing to work or business activities.
Language
Davaoeño, a dialectal variant of Cebuano, is the most widely spoken language in the city, while the Tagalog itself comes a distant second. English is the medium of instruction in schools and is widely understood and spoken especially in the business community and for all official documents. Bistaglish, an informal mixing of the above languages, is spoken as well.
- ЁЄ
- ЁЄ
- ЁЄ
- ЁЄ
- ЁЄ
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet\'\"\\(
- ЁЄryWvMVxeetщ\'\"\\(
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet














 ЧЪРкДхФФ ОпАЃЛѓДу ПРЧТ
ЧЪРкДхФФ ОпАЃЛѓДу ПРЧТ 13ГтПЌМг МвКёРкИИСЗ 1РЇ
13ГтПЌМг МвКёРкИИСЗ 1РЇ
 ГЛАд ИТДТ ОюЧаПј УЃБт
ГЛАд ИТДТ ОюЧаПј УЃБт
 ИЎОѓ ЧаБГ ЙцЙЎБт
ИЎОѓ ЧаБГ ЙцЙЎБт
 СжИЛПЁ ГЛАЁ ОЕ КёПыРК?
СжИЛПЁ ГЛАЁ ОЕ КёПыРК? УжАэАЁМККё РЬКЅЦЎ СёБтБт
УжАэАЁМККё РЬКЅЦЎ СёБтБт
 ЧіСіПЁМЕЕ ЧЪРкДхФФ!
ЧіСіПЁМЕЕ ЧЪРкДхФФ! ЧіСіПЁМ АЁДЩЧб
ЧіСіПЁМ АЁДЩЧб









 ЧЪРк ЦЏБо Ч§ХУ! ФСНУОюСі МКёНК
ЧЪРк ЦЏБо Ч§ХУ! ФСНУОюСі МКёНК
































