
-
МјРЇСІИёСЖШИМі
-
 И№ОЫ КИОЫ Йъ ЗЛЦЎЧЯБт~ ИЎСЖЦЎ ПЙОрБюСі
И№ОЫ КИОЫ Йъ ЗЛЦЎЧЯБт~ ИЎСЖЦЎ ПЙОрБюСі 89,158
89,158 -
 [ЧЪИЎЧЩ ММКЮ] ФЋИ№ХзНК ПЉЧр 100Йш СёБтБт
[ЧЪИЎЧЩ ММКЮ] ФЋИ№ХзНК ПЉЧр 100Йш СёБтБт 47,500
47,500 -
 ИЖДвЖѓ НУГЛ - ИЎРп АјПјСЄКИ. (ЛчСј 16Рх ЦїЧд)
ИЖДвЖѓ НУГЛ - ИЎРп АјПјСЄКИ. (ЛчСј 16Рх ЦїЧд) 30,586
30,586 -
 ММКЮРЧ СіПЊСЄКИ15,435
ММКЮРЧ СіПЊСЄКИ15,435 -
 ИЖДвЖѓ БйБГ - ЕћАЁРЬЕћРЬ ПЉЧр СЄКИ14,161
ИЖДвЖѓ БйБГ - ЕћАЁРЬЕћРЬ ПЉЧр СЄКИ14,161 -
 [ЧЪИЎЧЩ ММКЮ/ИЗХК] ШЃХк МїЙк ПфБн Йз СЄКИ13,179
[ЧЪИЎЧЩ ММКЮ/ИЗХК] ШЃХк МїЙк ПфБн Йз СЄКИ13,179 -
 КИЖѓФЋРЬРЧ И№Еч И№НРРЛ КММі РжДТ ЛчСјУИ.13,004
КИЖѓФЋРЬРЧ И№Еч И№НРРЛ КММі РжДТ ЛчСјУИ.13,004 -
 ИЖДвЖѓ БйБГ - ЦХЛѓЧб ЦјЦї ПЉЧрСЄКИ12,699
ИЖДвЖѓ БйБГ - ЦХЛѓЧб ЦјЦї ПЉЧрСЄКИ12,699 -
 [ММКЮ-ЙшМБТјРх] МБЙкШИЛч РќШЙјШЃПЁПф~12,270
[ММКЮ-ЙшМБТјРх] МБЙкШИЛч РќШЙјШЃПЁПф~12,270 -
 ИЖДвЖѓ СіПЊ(ПЁИЃЙЬХИ -ИЛЖѓХз)РЧ СіЕЕ/ЧбБЙ РННФСЁ/МюЧЮИє11,976
ИЖДвЖѓ СіПЊ(ПЁИЃЙЬХИ -ИЛЖѓХз)РЧ СіЕЕ/ЧбБЙ РННФСЁ/МюЧЮИє11,976
Cebu Map
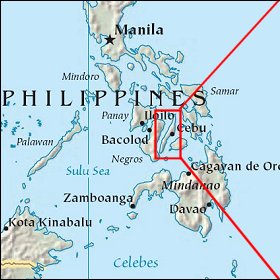
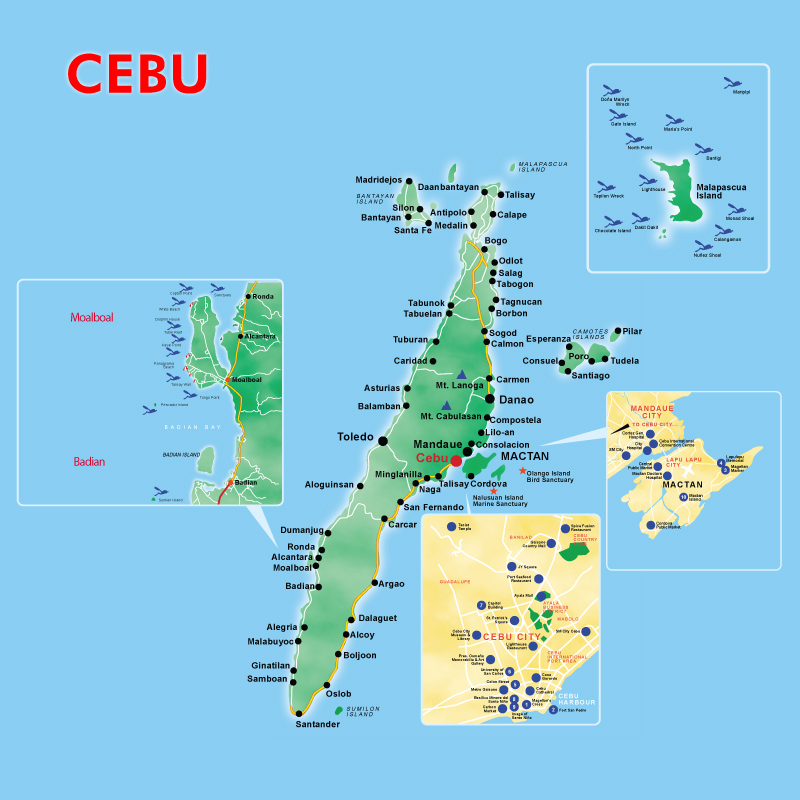

Cebu (Cebuano: Sugbo) is a province in the Philippines, consisting of Cebu Island and 167 surrounding islands. It is located to the east of Negros, to the west of Leyte and Bohol islands. Cebu is a long narrow island stretching 225 kilometers from north to south, surrounded by 167 neighbouring, smaller islands, which include Mactan, Bantayan, Malapascua, Olango and the Camotes Islands. Cebu has narrow coastlines, limestone plateaus and coastal plains. It also has rolling hills and rugged mountain ranges traversing the northern and southern lengths of the island. Cebu's highest mountains are over 1000 meters high. Flat tracts of land can be found in the city of Bogo and in the towns of San Remigio, Medellin and Daanbantayan at the northern region of the province. Its capital is Cebu City, the oldest city in the Philippines, which forms part of the Cebu Metropolitan Area together with four neighboring cities which include Danao City, Lapu-Lapu City, Mandaue City and Talisay City and eight other municipalities. Mactan-Cebu International Airport, located in Mactan island, is the second busiest airport in the Philippines.
Cebu is one of the most developed provinces in the Philippines, with Cebu City as the main center of commerce, trade, education and industry in the Visayas. Condé Nast Traveler Magazine named Cebu the seventh best island destination in the Indian Ocean-Asia region in 2007,[1] eighth best Asian-Pacific island destination in 2005, seventh in 2004 and in 2009.
Demographics
The population of Cebu in 2007 was 2,440,120, with its largest city accounting for 799,762 people, or more than a third of the entire provincial population.[2] Cebuano is the official language spoken in Cebu and it is also spoken in most areas of the Visayas, including Bohol, western Leyte, Negros Oriental and some provinces of Mindanao (Bukidnon, Agusan del Norte, Agusan del Sur, Davao del Norte, Davao del Sur, Davao Oriental, Davao City, Zamboanga del Norte, Zamboanga del Sur, Zamboanga Sibugay, Lanao del Norte, Misamis Oriental, Misamis Occidental, Camiguin, Compostela Valley, South Cotabato and Sarangani. The population of Central Visayas is predominantly young with about 37 percent of its population below 10 years old. This is very evident in the very broad base of the population pyramid in the region which has prevailed since 1970 but at a declining rate. A decline of 2.29 percentage points in the proportion of household population below 15 years old was noted from 1980 to 1995. Conversely, an increase of 3.06 percentage points was observed in the 15-64 age group during the same period. The population of the region is evenly distributed between male and female. However, the male population in the region has been increasing at a faster rate compared to the female population.[3]
Religion
The majority of its population are Roman Catholic,[4] there are also some followers of Islam, Buddhism and Hinduism.
The image of Santo Niño de Cebú (Holy Child of Cebu), the oldest Christian image in the Philippines, is enshrined and venerated at the Basilica of Santo Niño. According to Philippine historical documents, the statue of the Santo Niño (Holy Child) was given to the wife of the Rajah of Cebu by the Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan. The friendship is depicted in Cebu's cultural event, the Sinulog where street parades and loud drum beats preceded by a Christian mass is celebrated every third Sunday of January. Cebu has a Roman Catholic Archdiocese and has several major churches, including the Basilica Minor del Santo Niño de Cebu, Cebu Metropolitan Cathedral, Santo Rosario Parish Church, San José-Recoletos Church, Sacred Heart Church, Archdiocesan Shrine of Our Lady of Lourdes, National Shrine of Our Lady of the Rule, National Shrine of Saint Joseph, Archdiocesan Shrine of Our Lady of Guadalupe of Cebu and other Christian churches, as well as several other non-Catholic churches, mosques and temples.
Climate
Though Cebu has two official seasons, Dry and Wet, rainfall is usually not particularly high, with average rainfall hitting around 100 millimeters per month. The wet season usually comes from June to December, while the dry season comes from January until May. Rainfall is highest in June and July. Cebu's temperatures can reach a high of 36 degree celsius from March to May, to as low as 18 degrees at the mountains during the cooler season from October to January. The average temperature in Cebu is around 24 to 32 degree celsius, and does not fluctuate much except for the month of May, which is the hottest month. Cebu averages 70-80 percent humidity.
History
Between the 13th and 16th century Cebu then known as Zubu (or Sugbo) was an island inhabited by Hindu, animist and Muslim ruled by Rajahs and Datus. It was a kingdom of the defunct Rajahnate of Cebu.
The Rajahnate of Cebu was a native kingdom which used to exist in Cebu prior to the arrival of the Spaniards. It was founded by Sri 'Lumay' otherwise known as 'Rajamuda Lumaya', a native prince of the Chola dynasty which had invaded Sumatra in Indonesia. He was sent by the Maharajah to establish a base for expeditionary forces to subdue the local kingdoms, but he rebelled and established his own independent Rajahnate instead.
The arrival of Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan in 1521 established a period of Spanish exploration and colonization.
Losing favor for his plan of reaching the Spice Islands from king Manuel I of Portugal, by sailing west from Europe, Magellan offered his services to king Charles I of Spain. On September 20, 1519, Magellan led five ships with a crew of 250 people from the Spanish fort of Sanlúcar de Barrameda enroute to Southeast Asia via the Americas and Pacific Ocean. They reached the Philippines on March 16, 1521. Rajah Kolambu the king of Mazaua told them to sail for Cebu, where they could trade and have provisions.
Arriving in Cebu City, Magellan, with Enrique of Malacca as translator, befriended Rajah Humabon the Rajah or King of Cebu and persuaded the natives of allegiance to Charles I of Spain. Humabon and his wife were given Christian names and baptized as Carlos and Juana. The Santo Niño was presented to the native queen of Cebu, as a symbol of peace and friendship between the Spaniards and the Cebuanos. On April 14, Magellan erected a large wooden cross on the shores of Cebu. Afterwards, about 700 islanders were baptized.
Magellan soon heard of Datu Lapu-Lapu, a native king in nearby Mactan Island, a rival of the Rajahs of Cebu. It was thought that Humabon and Lapu-Lapu had been fighting for control of the flourishing trade in the area. On April 27, the Battle of Mactan occurred where the Spaniards were defeated and Magellan killed by the natives of Mactan[12] in Mactan Island. According to Italian historian and chronicler, Antonio Pigafetta, Magellan's body was never recovered despite efforts to trade for it with spice and jewels. Magellan's second in command, Juan Sebastián Elcano took his place as captain of the expedition and sailed their fleet back to Spain, circumnavigating the world.
Survivors of the Magellan expedition brought tales of a savage island in the East Indies with them when they returned to Spain. Consequently, several Spanish expeditions were sent to the islands but all ended in failure. In 1564, Spanish explorers led by Miguel López de Legazpi sailing from Mexico arrived in 1565 and established a colony.[13] The Spaniards fought the King Rajah Tupas and occupied his territories. The Spaniards established settlements, trade flourished and renamed the island to "Villa del Santíssimo Nombre de Jesús" (Town of the Most Holy Name of Jesus). Cebu became the first European settlement established by the Spanish Cortés in the Philippines. In 1595, the Universidad de San Carlos (University of San Carlos) was established and in 1860, Cebu opened its forts to foreign trade. The first printing house ("Imprenta de Escondrillas y Cia") was established in 1873 and in 1880, the Colegio de la Inmaculada Concepcion (College of the Immaculate Conception) was established and the first periodical The Bulletin of Cebu ("El Boletin de Cebú") began publishing in 1886. In 1898, the island was ceded to the United States after the Spanish-American War and Philippine-American War. In 1901, Cebu was governed by the United States for a brief period, however it became a charter province on February 24, 1937 and was governed independently by Filipino politicians.
Cebu, being one of the most densely populated island in the Philippines, served as a Japanese base during their occupation in World War II which began with the landing of Japanese soldiers in April 1942. The 3rd, 8th, 82nd and 85th Infantry Division of the Philippine Commonwealth Army was reestablished on 1942 to 1946 and the 8th Infantry Regiment of the Philippine Constabulary was reestablished again on 1944 to 1946 at the military general headquarters and the military camps and garrisoned in Cebu City and Cebu Province and started by the Anti-Japanese military operations in Cebu from April 1942 to September 1945 and helping Cebuano guerrillas and fought against the Japanese Imperial forces. Almost three years later in March 1945, combined Filipino and American forces landed and reoccupied the island during the liberation of the Philippines. Cebuano guerrilla groups led by an American, James Cushing is credited for the establishment of the Koga Papers which is said to have changed the American plans to retake the Philippines from Japanese occupation in 1944, by helping the combined United States and the Philippine Commonwealth Army forces enter Cebu in 1945. The following year the island achieved indepen
dence from colonial rule in 1946.
- ЁЄ
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet\'\"\\(
- ЁЄryWvMVxeetщ\'\"\\(
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet













 ЧЪРкДхФФ ОпАЃЛѓДу ПРЧТ
ЧЪРкДхФФ ОпАЃЛѓДу ПРЧТ 12ГтПЌМг МвКёРкИИСЗ 1РЇ
12ГтПЌМг МвКёРкИИСЗ 1РЇ
 ГЛАд ИТДТ ОюЧаПј УЃБт
ГЛАд ИТДТ ОюЧаПј УЃБт
 ИЎОѓ ЧаБГ ЙцЙЎБт
ИЎОѓ ЧаБГ ЙцЙЎБт
 СжИЛПЁ ГЛАЁ ОЕ КёПыРК?
СжИЛПЁ ГЛАЁ ОЕ КёПыРК? УжАэАЁМККё РЬКЅЦЎ СёБтБт
УжАэАЁМККё РЬКЅЦЎ СёБтБт
 ЧіСіПЁМЕЕ ЧЪРкДхФФ!
ЧіСіПЁМЕЕ ЧЪРкДхФФ! ЧіСіПЁМ АЁДЩЧб
ЧіСіПЁМ АЁДЩЧб









 ЧЪРк ЦЏБо Ч§ХУ! ФСНУОюСі МКёНК
ЧЪРк ЦЏБо Ч§ХУ! ФСНУОюСі МКёНК
































