
-
МјРЇСІИёСЖШИМі
-
 И№ОЫ КИОЫ Йъ ЗЛЦЎЧЯБт~ ИЎСЖЦЎ ПЙОрБюСі
И№ОЫ КИОЫ Йъ ЗЛЦЎЧЯБт~ ИЎСЖЦЎ ПЙОрБюСі 89,601
89,601 -
 [ЧЪИЎЧЩ ММКЮ] ФЋИ№ХзНК ПЉЧр 100Йш СёБтБт
[ЧЪИЎЧЩ ММКЮ] ФЋИ№ХзНК ПЉЧр 100Йш СёБтБт 49,745
49,745 -
 ИЖДвЖѓ НУГЛ - ИЎРп АјПјСЄКИ. (ЛчСј 16Рх ЦїЧд)
ИЖДвЖѓ НУГЛ - ИЎРп АјПјСЄКИ. (ЛчСј 16Рх ЦїЧд) 30,843
30,843 -
 ММКЮРЧ СіПЊСЄКИ15,559
ММКЮРЧ СіПЊСЄКИ15,559 -
 ИЖДвЖѓ БйБГ - ЕћАЁРЬЕћРЬ ПЉЧр СЄКИ14,395
ИЖДвЖѓ БйБГ - ЕћАЁРЬЕћРЬ ПЉЧр СЄКИ14,395 -
 [ЧЪИЎЧЩ ММКЮ/ИЗХК] ШЃХк МїЙк ПфБн Йз СЄКИ13,351
[ЧЪИЎЧЩ ММКЮ/ИЗХК] ШЃХк МїЙк ПфБн Йз СЄКИ13,351 -
 КИЖѓФЋРЬРЧ И№Еч И№НРРЛ КММі РжДТ ЛчСјУИ.13,165
КИЖѓФЋРЬРЧ И№Еч И№НРРЛ КММі РжДТ ЛчСјУИ.13,165 -
 ИЖДвЖѓ БйБГ - ЦХЛѓЧб ЦјЦї ПЉЧрСЄКИ12,865
ИЖДвЖѓ БйБГ - ЦХЛѓЧб ЦјЦї ПЉЧрСЄКИ12,865 -
 [ММКЮ-ЙшМБТјРх] МБЙкШИЛч РќШЙјШЃПЁПф~12,489
[ММКЮ-ЙшМБТјРх] МБЙкШИЛч РќШЙјШЃПЁПф~12,489 -
 ИЖДвЖѓ СіПЊ(ПЁИЃЙЬХИ -ИЛЖѓХз)РЧ СіЕЕ/ЧбБЙ РННФСЁ/МюЧЮИє12,144
ИЖДвЖѓ СіПЊ(ПЁИЃЙЬХИ -ИЛЖѓХз)РЧ СіЕЕ/ЧбБЙ РННФСЁ/МюЧЮИє12,144
Romblon Philippines
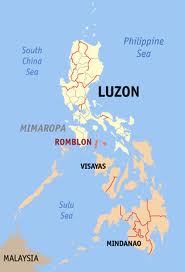
Romblon /rɒmˈbloʊn/rom-BLOHN is an island province of the Philippines located in the MIMAROPAregion. It lies south of Marinduque and Quezon, east of Mindoro, north of Aklan and Capiz, and west of Masbate. Its capital is also named Romblon. According the August 2007 Philippine census, it has a total population of 279,774. The province of Romblon is composed of three larger islands; Romblon Island at the center where the provincial capital is located, Tablas Island, west of the capital and Sibuyan Island, east of the capital. It also include smaller islands of Banton, Maestro de Campo, Simara, Carabao, Carlota and Isabel.
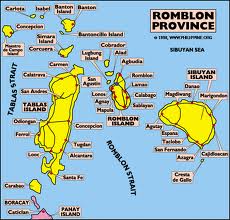
Approximately 187 nautical miles (346 km) south of Manila, the islands of Romblon lie on Sibuyan Sea, south of Marinduque Island and north of Panay Island. To the east is the island of Masbate and in the west, the island of Mindoro. The province is composed of three major islands: Romblon, where the capital city of Romblon is located, Tablas, the largest island in the province, and Sibuyan, the easternmost island. There are also four smaller island municipalities: Banton Island, Simara Island, Maestro de Campo Island, and Carabao Island.
Most of Romblon's islands have a mountainous and rugged topography, and are of volcanic origin. The highest elevation in the province is Mount Guiting-Guiting in Sibuyan, which stands at 2,058 m. The peak boasts one of the most challenging climbs in the country due to its jagged summit. Due to its geography, the province is endowed with lush vegetation and mineral resources. The fertile soil nurtures various agricultural activities. Being an archipelago, its coasts are dotted with numerous fine, white sand beaches such as in Carabao Island and Cresta del Gallo. Offshore, Romblon is a rich fishing ground. The islands lie on the migratory path of fishes from the Sulu and Visayan Seas, passing the Tablas Strait, Sibuyan Sea and Romblon Pass.
Romblon does not have a truly pronounced wet or dry season though the heaviest rainfall occurs from September to January. The driest months are March and April which are the best months to visit the province. 27ТА Celsius is the annual mean temperature, with February being the coldest month with temperatures dropping to 20ТА C, and May being the warmest month wherein temperatures could reach 35ТАC. Southwest monsoon winds or Habagat pass through the province from June to October while northeasterly winds or Amihan blows through the islands from December to February.
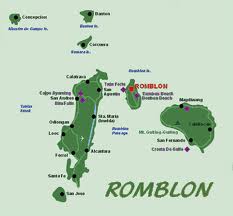
Romblon's early inhabitants were the Negritos from Panay and Mangyan tribes from Mindoro. Ancient wooden coffins discovered in caves of Banton Island in 1936 signify a rich ancient civilization and culture in the province before the arrival of the Spaniards. These artifacts are currently in display at the National Museum in Manila.
The islands were first colonized in 1570 by an expedition headed by Juan de Salcedo, nephew of conquistador Miguel Lopez de Legazpi. In 1853, it was organized into a politico-military district and made a sub-province of Capiz.In 1917, after American colonial rule was established in the Philippines, it was converted into a separate province by Philippine Act No. 2724.It was returned under the control of Capiz during the Japanese occupation of the Philippines. On January 1, 1947, following the liberation of the Philippines, the regular provincial status of Romblon was restored.The province of Romblon has a mainly agricultural economy with copra farming, fishing, and rice farming as the chief agricultural activities. The fertile soil nurtures various agricultural crops like coconut, rice, corn, bananas, raffia palm, root crops, fruit trees, and many others. Its abundant fishing grounds supplies fish to various distribution centers in Batangas and Quezon province. Mining is also a lucrative industry in the province due to its vast mineral resources. Aside from marble, the islands are rich in granite, nickel, silica, mercury, zinc, copper, silver, limestone, sulfide, ores, kaolin, clay, magnesium, and quartz. Gold panning sites have sprouted in some of the mountain stream areas in Magdiwang, Sibuyan Island. In recent years, tourism also becoming a viable source of income for the province as its pristine beaches and crystal clear waters attract local and foreign tourists to visit and experience its physical beauty and culture.
- ЁЄ
- ЁЄ
- ЁЄ
- ЁЄ
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet\'\"\\(
- ЁЄryWvMVxeetщ\'\"\\(
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet













 ЧЪРкДхФФ ОпАЃЛѓДу ПРЧТ
ЧЪРкДхФФ ОпАЃЛѓДу ПРЧТ 13ГтПЌМг МвКёРкИИСЗ 1РЇ
13ГтПЌМг МвКёРкИИСЗ 1РЇ

 ГЛАд ИТДТ ОюЧаПј УЃБт
ГЛАд ИТДТ ОюЧаПј УЃБт
 ИЎОѓ ЧаБГ ЙцЙЎБт
ИЎОѓ ЧаБГ ЙцЙЎБт
 СжИЛПЁ ГЛАЁ ОЕ КёПыРК?
СжИЛПЁ ГЛАЁ ОЕ КёПыРК? УжАэАЁМККё РЬКЅЦЎ СёБтБт
УжАэАЁМККё РЬКЅЦЎ СёБтБт
 ЧіСіПЁМЕЕ ЧЪРкДхФФ!
ЧіСіПЁМЕЕ ЧЪРкДхФФ! ЧіСіПЁМ АЁДЩЧб
ЧіСіПЁМ АЁДЩЧб









 ЧЪРк ЦЏБо Ч§ХУ! ФСНУОюСі МКёНК
ЧЪРк ЦЏБо Ч§ХУ! ФСНУОюСі МКёНК
































