
-
МјРЇСІИёСЖШИМі
-
 И№ОЫ КИОЫ Йъ ЗЛЦЎЧЯБт~ ИЎСЖЦЎ ПЙОрБюСі
И№ОЫ КИОЫ Йъ ЗЛЦЎЧЯБт~ ИЎСЖЦЎ ПЙОрБюСі 89,457
89,457 -
 [ЧЪИЎЧЩ ММКЮ] ФЋИ№ХзНК ПЉЧр 100Йш СёБтБт
[ЧЪИЎЧЩ ММКЮ] ФЋИ№ХзНК ПЉЧр 100Йш СёБтБт 48,905
48,905 -
 ИЖДвЖѓ НУГЛ - ИЎРп АјПјСЄКИ. (ЛчСј 16Рх ЦїЧд)
ИЖДвЖѓ НУГЛ - ИЎРп АјПјСЄКИ. (ЛчСј 16Рх ЦїЧд) 30,790
30,790 -
 ММКЮРЧ СіПЊСЄКИ15,529
ММКЮРЧ СіПЊСЄКИ15,529 -
 ИЖДвЖѓ БйБГ - ЕћАЁРЬЕћРЬ ПЉЧр СЄКИ14,341
ИЖДвЖѓ БйБГ - ЕћАЁРЬЕћРЬ ПЉЧр СЄКИ14,341 -
 [ЧЪИЎЧЩ ММКЮ/ИЗХК] ШЃХк МїЙк ПфБн Йз СЄКИ13,319
[ЧЪИЎЧЩ ММКЮ/ИЗХК] ШЃХк МїЙк ПфБн Йз СЄКИ13,319 -
 КИЖѓФЋРЬРЧ И№Еч И№НРРЛ КММі РжДТ ЛчСјУИ.13,132
КИЖѓФЋРЬРЧ И№Еч И№НРРЛ КММі РжДТ ЛчСјУИ.13,132 -
 ИЖДвЖѓ БйБГ - ЦХЛѓЧб ЦјЦї ПЉЧрСЄКИ12,831
ИЖДвЖѓ БйБГ - ЦХЛѓЧб ЦјЦї ПЉЧрСЄКИ12,831 -
 [ММКЮ-ЙшМБТјРх] МБЙкШИЛч РќШЙјШЃПЁПф~12,445
[ММКЮ-ЙшМБТјРх] МБЙкШИЛч РќШЙјШЃПЁПф~12,445 -
 ИЖДвЖѓ СіПЊ(ПЁИЃЙЬХИ -ИЛЖѓХз)РЧ СіЕЕ/ЧбБЙ РННФСЁ/МюЧЮИє12,113
ИЖДвЖѓ СіПЊ(ПЁИЃЙЬХИ -ИЛЖѓХз)РЧ СіЕЕ/ЧбБЙ РННФСЁ/МюЧЮИє12,113
Aklan
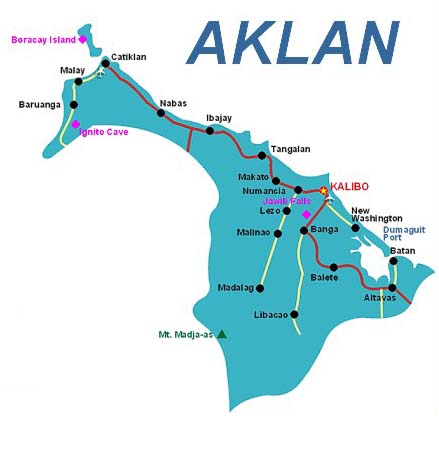
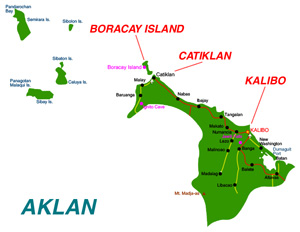
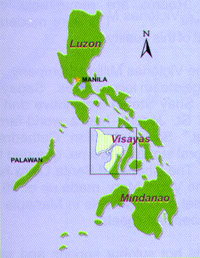
Aklan is a province of the Philippines in the Western Visayas. Its capital is Kalibo. It is in the northwest portion of Panay Island, bordering Antique Province to the southwest, and Capiz Province to the east. Aklan faces the Sibuyan Sea and Romblon Province to the north.
History
Aklan is considered to be the oldest province in the country and is believed to have been established in the 12th century by settlers from Borneo ruled by the chieftain Datu Dinagandan which traded with its neighbouring islands.
Towards the end of the 14th century, Datu Dinagandan moved the capital from what is now Batan. In 1433, Datu Kalantiaw's grandson and successor, Datu Kalantiaw III, was said to have formulated a set of laws known today as the Code of Kalantiaw. Well respected scholarly long-term Philippine resident historian William Henry Scott, proved these "laws" to be a total fabrication.[1][2][3][4] In 1437, the short-lived dynasty of Datu Kalantiaw ended when Datu Kalantiaw III was killed in battle with the tribes of Datu Manduyog, the legitimate successor of Datu Dinagandan. When Datu Manduyog became the new chieftain, he moved the capital to Bakan (now known as Banga).
Several datus succeeded Datu Manduyog until the Spanish explorer Miguel López de Legazpi landed in Batan in 1565 and claimed the island for Spain. Datu Kabanyag was the chieftain at that period and had his capital in Libacao.
In 1942, the Japanese invaded Aklan during World War II and in 1945, combined Filipino and American army along with Aklanon guerrillas liberated Aklan during the war in the Pacific.
Aklan finally became a separate province through Republic Act No. 1414 signed by President Magsaysay on April 25, 1956, separating Aklan from Capiz.[5] The original towns were Altavas, Balete, Batan, Banga, Buruanga, Ibajay, Kalibo, Lezo, Libacao, Madalag, Malay, Makato, Malinao, Nabas, New Washington, Numancia, and Tangalan, then all part of the province of Capiz.
This law was authored by Congressman Godofredo P. Ramos and the province was inaugurated on November 8, 1956. Ramos became the first congressman of Aklan, he was succeeded by José B. Legaspi. The third congressman, serving until the declaration of martial law in 1972, was Rafael B. Legaspi. José Raz Menez was appointed the first governor of Aklan by President Magsaysay and he served until December 30, 1959. In 1960, Godofredo P. Ramos became the first elected governor but upon resigning to run for Congress he was succeeded by the vice governor, Virgilio S. Patricio. In 1964, José B. Legaspi succeeded Patricio and he held office for two consecutive terms from 1964 to 1971.
Ethnic groups
The main inhabitants of the province are the Aklanon, who are part of the Visayan ethnic group. Other inhabitants include the Negrito, locally known as the Ati and the Sulod, a lesser known tribal group living in the hinterlands of Panay. Other Visayans are also present such as the Karay-a, the Hiligaynon and the Capiznon.
Languages
The most prominent languages in the province are Akeanon (Aklanon Proper), Malaynon and Buruanganon. Akeanon is spoken by a majority of the people, while Malaynon is spoken in Malay and Buruanganon is spoken in Buruanga, Aklan . Other regional languages used include;
Religion
Roman Catholicism is the dominant religion of the people and Christian festivals such as Christmas and Lent are regarded with high importance. Meanwhile, Christian icons such as the Santo Niño are regarded as cultural symbols of the people. Animism, however, is still practised by the Ati.
Culture
Despite the prevalence of Christianity native beliefs about the aswang and the babaylan are still prevalent among the people. Kulam or witchcraft, locally known as "amulit" is still feared by many residents.
- ЁЄ
- ЁЄ
- ЁЄ
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet\'\"\\(
- ЁЄryWvMVxeetщ\'\"\\(
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet














 ЧЪРкДхФФ ОпАЃЛѓДу ПРЧТ
ЧЪРкДхФФ ОпАЃЛѓДу ПРЧТ 12ГтПЌМг МвКёРкИИСЗ 1РЇ
12ГтПЌМг МвКёРкИИСЗ 1РЇ
 ГЛАд ИТДТ ОюЧаПј УЃБт
ГЛАд ИТДТ ОюЧаПј УЃБт
 ИЎОѓ ЧаБГ ЙцЙЎБт
ИЎОѓ ЧаБГ ЙцЙЎБт
 СжИЛПЁ ГЛАЁ ОЕ КёПыРК?
СжИЛПЁ ГЛАЁ ОЕ КёПыРК? УжАэАЁМККё РЬКЅЦЎ СёБтБт
УжАэАЁМККё РЬКЅЦЎ СёБтБт
 ЧіСіПЁМЕЕ ЧЪРкДхФФ!
ЧіСіПЁМЕЕ ЧЪРкДхФФ! ЧіСіПЁМ АЁДЩЧб
ЧіСіПЁМ АЁДЩЧб









 ЧЪРк ЦЏБо Ч§ХУ! ФСНУОюСі МКёНК
ЧЪРк ЦЏБо Ч§ХУ! ФСНУОюСі МКёНК
































