
-
МјРЇСІИёСЖШИМі
-
 Malacañang Palace-Official Residence of the Pres
Malacañang Palace-Official Residence of the Pres 138,879
138,879 -
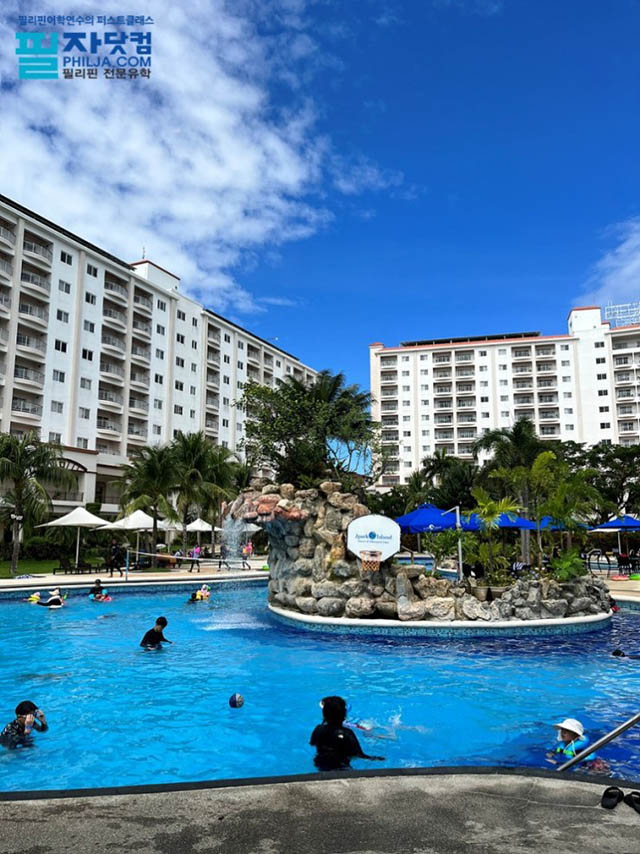
 Amana Water Park
Amana Water Park 115,400
115,400 -
 IFUGAO TRIBE
IFUGAO TRIBE 109,383
109,383 -
 Santacruzan-The Queen of all Filipino Festivals109,270
Santacruzan-The Queen of all Filipino Festivals109,270 -
 Water Refilling Station: an alternative source of drink107,159
Water Refilling Station: an alternative source of drink107,159 -
 LAMBANOG-THE POOR MAN\'S DRINK104,512
LAMBANOG-THE POOR MAN\'S DRINK104,512 -
 Christmas Parol [lantern in English]104,359
Christmas Parol [lantern in English]104,359 -
 HANGING RICE97,032
HANGING RICE97,032 -
 Taoist Temple93,994
Taoist Temple93,994 -
 Corn Fields in the Philippines90,466
Corn Fields in the Philippines90,466
COCONUT TIMBER

Coconut timber is a hardwood-substitute from coconut palm trees.
It is referred to in the Philippines as coconut lumber
and elsewhere additionally as cocowood.
It is a new timber resource that comes from plantation crops and offers an alternative
to rainforest timber.

Characteristics:
Its wood is reminiscent in appearance to mahogany; however, coconut timber has a much more fibrous grain than mahogany and lacks mahogany's iridescence.
Colour tones and hues range from golden to near ebony, with dark brown flecks.
There are three basic colour divisions relating to the timber's density:
dark brown tones (high density); medium brown tones (medium density); and light golden tones
(low density).
Coconut trunk, showing typical "grain" of coconut wood

Coconut timber or coconut lumber has many applications as both a structural
and interior design material.
One of primary uses of coconut timber is for building construction.
Coconut timber is suitable for housing components like trusses,
purlins, walls, joists, doors, window frames and jalousies.


Coconut wood can be a promising material for the manufacture of furniture, novelties
and other handicrafts due to its beautiful grain and attractive natural appearance.


Coconut palace in Philippines
The harder, high-density timber is suitable for general structural purposes such as pillars, trusses,
rafting, furniture, window and door frames, floors, decking and floor joists.
Medium density coconut timber can be used for walls,
ceiling joists and horizontal studs.
Low density coconut timber is used in non-load bearing applications like wood panelling,
internal trim and ceilings, as well as homewares.
Coconut timber is a source of income for less developed south pacific island communities.
The previously low value senile coconut trunks have been promoted as a source of veneer and other wood products.
- ЁЄfYGbJbhcBF

- ЁЄfYGbJbhcBF

- ЁЄfYGbJbhcBF

- ЁЄfYGbJbhcBF

- ЁЄfYGbJbhcBF

- ЁЄfYGbJbhcBF

- ЁЄfYGbJbhcBF

- ЁЄfYGbJbhcBF

- ЁЄfYGbJbhcBF

- ЁЄfYGbJbhcBF

- ЁЄfYGbJbhcBF

- ЁЄfYGbJbhcBF

- ЁЄfYGbJbhcBF

- ЁЄfYGbJbhcBF

- ЁЄfYGbJbhcBF




- ЁЄSaDEVEqmgq

- ЁЄSaDEVEqmgq

- ЁЄSaDEVEqmgq\'\"\\(

- ЁЄSaDEVEqmgqщ\'\"\\(

- ЁЄSaDEVEqmgq

- ЁЄSaDEVEqmgq

- ЁЄSaDEVEqmgq

- ЁЄSaDEVEqmgq

- ЁЄSaDEVEqmgq

- ЁЄSaDEVEqmgq

- ЁЄSaDEVEqmgq

- ЁЄSaDEVEqmgq

- ЁЄSaDEVEqmgq

- ЁЄSaDEVEqmgq

- ЁЄSaDEVEqmgq




- ЁЄqpvwYmzPrC

- ЁЄqpvwYmzPrC

- ЁЄqpvwYmzPrC

- ЁЄqpvwYmzPrC

- ЁЄqpvwYmzPrC

- ЁЄqpvwYmzPrC

- ЁЄqpvwYmzPrC

- ЁЄqpvwYmzPrC

- ЁЄqpvwYmzPrC\'\"\\(

- ЁЄqpvwYmzPrCщ\'\"\\(

- ЁЄqpvwYmzPrC

- ЁЄqpvwYmzPrC

- ЁЄqpvwYmzPrC

- ЁЄqpvwYmzPrC

- ЁЄqpvwYmzPrC












 ЧЪРкДхФФ ОпАЃЛѓДу ПРЧТ
ЧЪРкДхФФ ОпАЃЛѓДу ПРЧТ 11ГтПЌМг МвКёРкИИСЗ 1РЇ
11ГтПЌМг МвКёРкИИСЗ 1РЇ
 ГЛАд ИТДТ ОюЧаПј УЃБт
ГЛАд ИТДТ ОюЧаПј УЃБт
 ИЎОѓ ЧаБГ ЙцЙЎБт
ИЎОѓ ЧаБГ ЙцЙЎБт
 СжИЛПЁ ГЛАЁ ОЕ КёПыРК?
СжИЛПЁ ГЛАЁ ОЕ КёПыРК? УжАэАЁМККё РЬКЅЦЎ СёБтБт
УжАэАЁМККё РЬКЅЦЎ СёБтБт
 ЧіСіПЁМЕЕ ЧЪРкДхФФ!
ЧіСіПЁМЕЕ ЧЪРкДхФФ! ЧіСіПЁМ АЁДЩЧб
ЧіСіПЁМ АЁДЩЧб









 ЧЪРк ЦЏБо Ч§ХУ! ФСНУОюСі МКёНК
ЧЪРк ЦЏБо Ч§ХУ! ФСНУОюСі МКёНК


 АЁСЗПЌМіЗЮ ДйЧдАд ОзЦМКёЦМ
АЁСЗПЌМіЗЮ ДйЧдАд ОзЦМКёЦМ





























