
-
МјРЇСІИёСЖШИМі
-
 Malacañang Palace-Official Residence of the Pres
Malacañang Palace-Official Residence of the Pres 138,879
138,879 -
 Amana Water Park
Amana Water Park 115,400
115,400 -
 IFUGAO TRIBE
IFUGAO TRIBE 109,383
109,383 -
 Santacruzan-The Queen of all Filipino Festivals109,270
Santacruzan-The Queen of all Filipino Festivals109,270 -
 Water Refilling Station: an alternative source of drink107,159
Water Refilling Station: an alternative source of drink107,159 -
 LAMBANOG-THE POOR MAN\'S DRINK104,512
LAMBANOG-THE POOR MAN\'S DRINK104,512 -
 Christmas Parol [lantern in English]104,359
Christmas Parol [lantern in English]104,359 -
 HANGING RICE97,032
HANGING RICE97,032 -
 Taoist Temple93,994
Taoist Temple93,994 -
 Corn Fields in the Philippines90,466
Corn Fields in the Philippines90,466
MAKING ABACA FIBER

Abaca fiber is extracted from the leaf sheath around the base of the abaca plant. Harvesting of abaca stalks
usually takes place between 18 and 24 months from the first shoots.
When mature, an abaca plant will have about 12 to 30 leaf stalks,
each approximately 12 to 20 feet high. Subsequent harvest is done at 3 to 4 month intervals.
There are two stages in the harvesting process:
(1) topping, when the leaf stalks are cut at the base of the petiole
with a knife or a sickle.
(2) tumbling, when the stalks are tumbled down with the use of a bolo knife.


After tumbling, the cut stalks are put in a pile, ready for the next step:
Tuxying.

Tuxying is the process of extracting the fiber from the leaf sheaths.
A specially-made tuxying knife is used to make an
incision through the inner and middle layer of each sheath,
close to the base or butt end to remove the outer layer.
The strips, or ЁАtuxiesЁБ, obtained from this process are then put through a
cleaning process, called stripping, in which all
pulpy material is scraped off and the strands of fiber are freed.
In the Philippines, the two common stripping methods in use are
hand-stripping and spindle stripping.
Hand-stripping (hagotan) is a simple yet laborious method. The strip, or tuxy, is inserted between a block and the stripping knife, then pulled with force
from the tip end of the tuxy to separate the fiber from any waste.

The spindle stripping method involves winding the fibers around a
tapered-shaped spindle which is kept in motion by an electric motor or
an engine. A spindle stripped fiber tends to be whiter and more lustrous than a corresponding grade of hand stripped fiber.


The abaca fibers are then left out to dry naturally in the sun.


Once the abaca fibers have dried out sufficiently, they are transported to a warehouse where they are sorted according to quality.

The best grades of abaca are fine, lustrous, light beige in colour and very
strong. The official standard grades of abaca fiber are divided into three
classes depending on the manner of extraction: hand-stripping, spindle-stripping or decortication. Quality is then determined by colour, texture,
fiber length, strength, and cleaning, which is a direct result of the stripping method and knife used.

- ЁЄfYGbJbhcBF

- ЁЄfYGbJbhcBF

- ЁЄfYGbJbhcBF

- ЁЄfYGbJbhcBF

- ЁЄfYGbJbhcBF

- ЁЄfYGbJbhcBF

- ЁЄfYGbJbhcBF

- ЁЄfYGbJbhcBF

- ЁЄfYGbJbhcBF

- ЁЄfYGbJbhcBF

- ЁЄfYGbJbhcBF

- ЁЄfYGbJbhcBF

- ЁЄfYGbJbhcBF

- ЁЄfYGbJbhcBF

- ЁЄfYGbJbhcBF




- ЁЄSaDEVEqmgq

- ЁЄSaDEVEqmgq

- ЁЄSaDEVEqmgq\'\"\\(

- ЁЄSaDEVEqmgqщ\'\"\\(

- ЁЄSaDEVEqmgq

- ЁЄSaDEVEqmgq

- ЁЄSaDEVEqmgq

- ЁЄSaDEVEqmgq

- ЁЄSaDEVEqmgq

- ЁЄSaDEVEqmgq

- ЁЄSaDEVEqmgq

- ЁЄSaDEVEqmgq

- ЁЄSaDEVEqmgq

- ЁЄSaDEVEqmgq

- ЁЄSaDEVEqmgq




- ЁЄqpvwYmzPrC

- ЁЄqpvwYmzPrC

- ЁЄqpvwYmzPrC

- ЁЄqpvwYmzPrC

- ЁЄqpvwYmzPrC

- ЁЄqpvwYmzPrC

- ЁЄqpvwYmzPrC

- ЁЄqpvwYmzPrC

- ЁЄqpvwYmzPrC\'\"\\(

- ЁЄqpvwYmzPrCщ\'\"\\(

- ЁЄqpvwYmzPrC

- ЁЄqpvwYmzPrC

- ЁЄqpvwYmzPrC

- ЁЄqpvwYmzPrC

- ЁЄqpvwYmzPrC












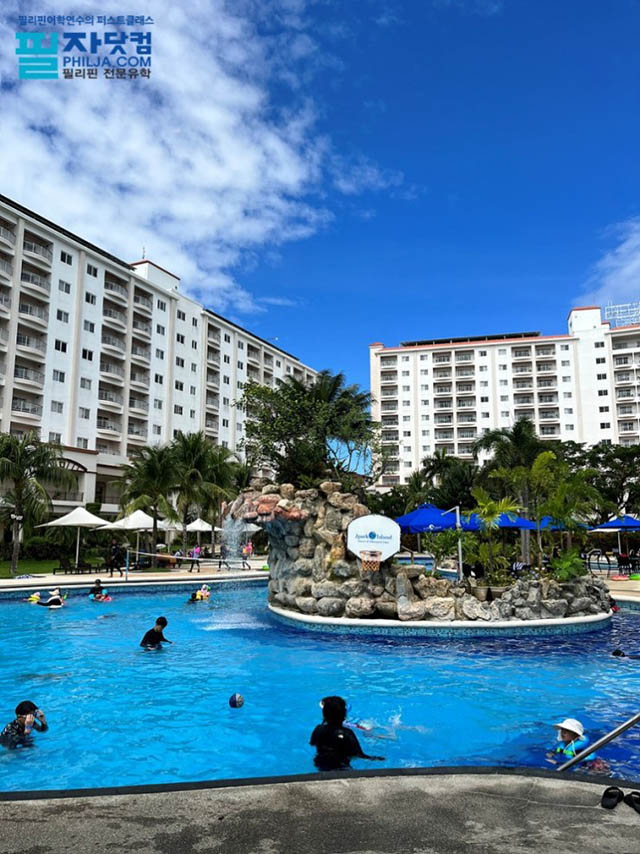
 ЧЪРкДхФФ ОпАЃЛѓДу ПРЧТ
ЧЪРкДхФФ ОпАЃЛѓДу ПРЧТ 11ГтПЌМг МвКёРкИИСЗ 1РЇ
11ГтПЌМг МвКёРкИИСЗ 1РЇ
 ГЛАд ИТДТ ОюЧаПј УЃБт
ГЛАд ИТДТ ОюЧаПј УЃБт
 ИЎОѓ ЧаБГ ЙцЙЎБт
ИЎОѓ ЧаБГ ЙцЙЎБт
 СжИЛПЁ ГЛАЁ ОЕ КёПыРК?
СжИЛПЁ ГЛАЁ ОЕ КёПыРК? УжАэАЁМККё РЬКЅЦЎ СёБтБт
УжАэАЁМККё РЬКЅЦЎ СёБтБт
 ЧіСіПЁМЕЕ ЧЪРкДхФФ!
ЧіСіПЁМЕЕ ЧЪРкДхФФ! ЧіСіПЁМ АЁДЩЧб
ЧіСіПЁМ АЁДЩЧб









 ЧЪРк ЦЏБо Ч§ХУ! ФСНУОюСі МКёНК
ЧЪРк ЦЏБо Ч§ХУ! ФСНУОюСі МКёНК


 АЁСЗПЌМіЗЮ ДйЧдАд ОзЦМКёЦМ
АЁСЗПЌМіЗЮ ДйЧдАд ОзЦМКёЦМ





























