
-
МјРЇСІИёСЖШИМі
-
 И№ОЫ КИОЫ Йъ ЗЛЦЎЧЯБт~ ИЎСЖЦЎ ПЙОрБюСі
И№ОЫ КИОЫ Йъ ЗЛЦЎЧЯБт~ ИЎСЖЦЎ ПЙОрБюСі 89,457
89,457 -
 [ЧЪИЎЧЩ ММКЮ] ФЋИ№ХзНК ПЉЧр 100Йш СёБтБт
[ЧЪИЎЧЩ ММКЮ] ФЋИ№ХзНК ПЉЧр 100Йш СёБтБт 48,903
48,903 -
 ИЖДвЖѓ НУГЛ - ИЎРп АјПјСЄКИ. (ЛчСј 16Рх ЦїЧд)
ИЖДвЖѓ НУГЛ - ИЎРп АјПјСЄКИ. (ЛчСј 16Рх ЦїЧд) 30,789
30,789 -
 ММКЮРЧ СіПЊСЄКИ15,529
ММКЮРЧ СіПЊСЄКИ15,529 -
 ИЖДвЖѓ БйБГ - ЕћАЁРЬЕћРЬ ПЉЧр СЄКИ14,341
ИЖДвЖѓ БйБГ - ЕћАЁРЬЕћРЬ ПЉЧр СЄКИ14,341 -
 [ЧЪИЎЧЩ ММКЮ/ИЗХК] ШЃХк МїЙк ПфБн Йз СЄКИ13,319
[ЧЪИЎЧЩ ММКЮ/ИЗХК] ШЃХк МїЙк ПфБн Йз СЄКИ13,319 -
 КИЖѓФЋРЬРЧ И№Еч И№НРРЛ КММі РжДТ ЛчСјУИ.13,132
КИЖѓФЋРЬРЧ И№Еч И№НРРЛ КММі РжДТ ЛчСјУИ.13,132 -
 ИЖДвЖѓ БйБГ - ЦХЛѓЧб ЦјЦї ПЉЧрСЄКИ12,831
ИЖДвЖѓ БйБГ - ЦХЛѓЧб ЦјЦї ПЉЧрСЄКИ12,831 -
 [ММКЮ-ЙшМБТјРх] МБЙкШИЛч РќШЙјШЃПЁПф~12,445
[ММКЮ-ЙшМБТјРх] МБЙкШИЛч РќШЙјШЃПЁПф~12,445 -
 ИЖДвЖѓ СіПЊ(ПЁИЃЙЬХИ -ИЛЖѓХз)РЧ СіЕЕ/ЧбБЙ РННФСЁ/МюЧЮИє12,112
ИЖДвЖѓ СіПЊ(ПЁИЃЙЬХИ -ИЛЖѓХз)РЧ СіЕЕ/ЧбБЙ РННФСЁ/МюЧЮИє12,112
Sulu Philippines Map
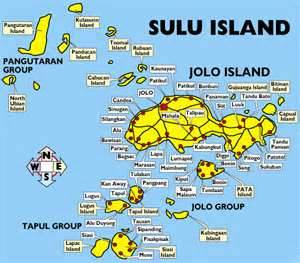
Sulu (Tausūg: سوگ, Sūg) is an autonomous island province of the Philippines located in the Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (ARMM). Its capital is Jolo and occupies the middle group of islands of the Sulu Archipelago, between Basilan and Tawi-Tawi. It is home to the historical Sultanate of Sulu.
History
The peaceful advent of Islam around 1138 through merchants and traders had a distinct influence on Southeast Asia. The coming of Arabs, Persians and other Muslims paved the way for the arrival of religious missionaries, traders, scholars and travelers to Sulu and Mindanao in the 12th century.
A landmark born of the social process was the founding of the principality of Buansa Sumatra, who settled there and married the daughter. A decade earlier (1380), Karim-ul-Mahkdum, an Arab religious missionary and learned judge, reinforced the Islamic foundation of Rajah Baguindaтs polity (1390–1460) and that of the Sultanate of Sayid Abubakar, princely scholar from Arabia who married Paramisuli, the daughter of Rajah Baguinda. Sayid Abubakar eventually inherited the rule of Rajah Baguinda, established the Sultanate and became the first Sultan of Sulu. To consolidate his rule, Sayid Abubakar united the local political units under the umbrella of the Sultanate. He brought Sulu, Zamboanga Peninsula, Palawan and Basilan under its aegis.
The navigational error that landed Ferdinand Magellan to Limasawa brought the Philippines to the awareness of Europe and opened the door to Spanish colonial incursion. The Spaniards introduced Christianity and a political system of church-state dichotomy encountering fierce resistance in the devastating Moro wars from 1578 to 1899.
After Spain ceded the Philippines to the United States, American forces came to Jolo and ended the 23 years of Spanish military occupation (1876- to 1899). On August 20, Sultan Jamalul Kiram II and Brig. Gen John C. Bates signed the Bates Agreement that continued the gradual emasculation of the Sultanate started by Spain (Treaty of 1878) until its final inertia on March 1915 when the Sultan abdicated his temporal powers in the Carpenter Agreement. The Agreement totally vanished opposition against the civilian government of Gov. Clinton Solidum.
The Department of Mindanao and Sulu under Gov. Carpenter was created by Philippine Commission Act 2309 (1914) and ended on February 5, 1920 by Act of Philippine Legislature No. 2878. The Bureau of Non-Christian Tribes was organized and briefly headed by Teofisto Guingona, Sr. With the enactment by the US Congress of the Jones Law (Philippine Autonomy Law) in 1916, ultimate Philippine independence was guaranteed and the Filipinization of public administration began. Sulu, however, had an appointed American governor until 1935 and the Governor General in Manila had a say in Sulu affairs. At any rate, the essence of local governance forged by Rajah Baguinda continued to permeate the ethos of Sulu politics despite centuries of colonial presence. History points to a local government in Sulu that antedates other similar systems in the country. Today, Sulu has a locally constituted government under the new leadership of Governor Benjamin T. Loong and is part of the ARMM.
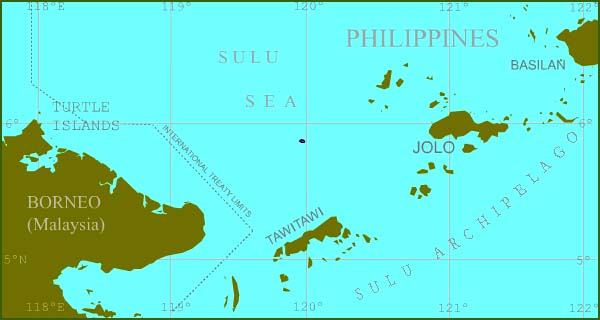
Geography
Sulu's main island, Jolo is 15th largest island of the Philippine Archipelago in terms of the area, spanning 1,600 square kilometers. Sulu is a part of the Sulu Archipelago, which stretches from the tip of the Zamboanga Peninsula to the island of Borneo. The main island and also its islets are located between the island-provinces of Basilan to the northeast, and Tawi-Tawi to the southwest.
People and culture
Although consisting of a mixed community of Muslims and Christians, the Tausug dominate the Sulu Archipelago. The Tausug were among the first inhabitants of the Philippines to embrace Islam as a religion and a way of life.
Their traditional religio-political structure is the sultanate. The sultan is the head of all ranks. Succession is by election by his staff, although patrilineal succession is the ideal.
The Tausug are referred to as тpeople of the currentт, reflective of their close ties to the sea. The handicrafts of Sulu have both Islamic and Malay influences. Skilled artisans make boats, bladed weapons, bronze and brassware, pis cloth, embroidered textiles, shellcraft, traditional house carvings, and carved wooden grave markers.
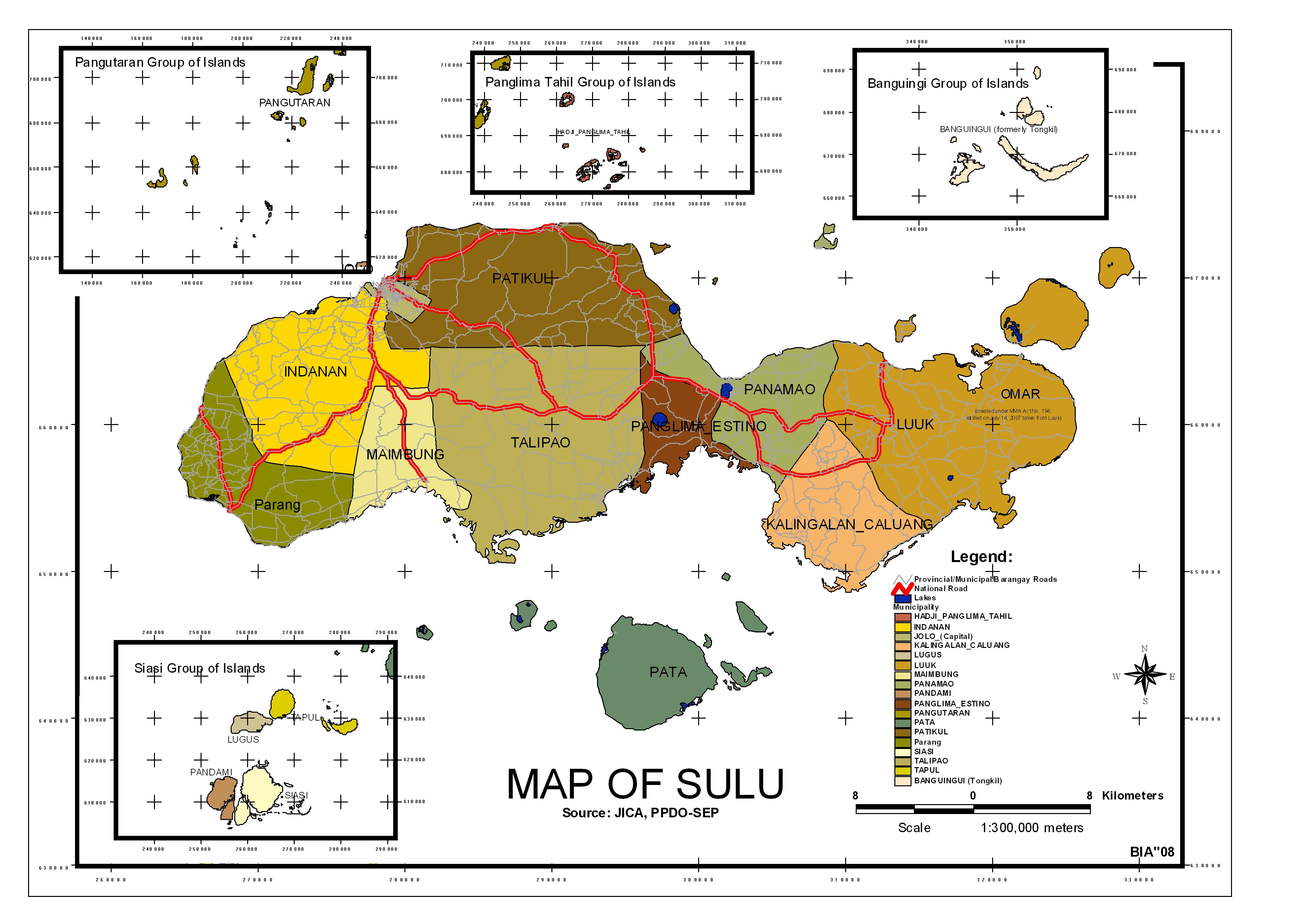
Economy
The province of Sulu is predominantly agricultural with farming and fishing as its main livelihood activities. Its fertile soil and ideal climate can grow a variety of crops such as abaca, coconuts, oranges, and lanzones as well as exotic fruits seldom found elsewhere in the country such as durian and mangosteen.
Fishing is the most important industry since the Sulu Sea is one of the richest fishing grounds in the country. The province also have an extensive pearl industry. Pearls are extensively gathered and a pearl farm is established at Marungas Island. The backs of sea turtles are made into beautiful trays and combs. During breaks from fishing, the people build boats and weave mats. Other industries include coffee processing and fruit preservation.
- ЁЄ
- ЁЄ
- ЁЄ
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet\'\"\\(
- ЁЄryWvMVxeetщ\'\"\\(
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet
- ЁЄryWvMVxeet














 ЧЪРкДхФФ ОпАЃЛѓДу ПРЧТ
ЧЪРкДхФФ ОпАЃЛѓДу ПРЧТ 12ГтПЌМг МвКёРкИИСЗ 1РЇ
12ГтПЌМг МвКёРкИИСЗ 1РЇ
 ГЛАд ИТДТ ОюЧаПј УЃБт
ГЛАд ИТДТ ОюЧаПј УЃБт
 ИЎОѓ ЧаБГ ЙцЙЎБт
ИЎОѓ ЧаБГ ЙцЙЎБт
 СжИЛПЁ ГЛАЁ ОЕ КёПыРК?
СжИЛПЁ ГЛАЁ ОЕ КёПыРК? УжАэАЁМККё РЬКЅЦЎ СёБтБт
УжАэАЁМККё РЬКЅЦЎ СёБтБт
 ЧіСіПЁМЕЕ ЧЪРкДхФФ!
ЧіСіПЁМЕЕ ЧЪРкДхФФ! ЧіСіПЁМ АЁДЩЧб
ЧіСіПЁМ АЁДЩЧб









 ЧЪРк ЦЏБо Ч§ХУ! ФСНУОюСі МКёНК
ЧЪРк ЦЏБо Ч§ХУ! ФСНУОюСі МКёНК
































